Art has always been a reflection of human creativity, culture, and emotions. With the rise of artificial intelligence, a new form of artistic expression is emerging – AI-generated art. This innovative medium is transforming the art world, offering a wealth of benefits and unique challenges. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of AI-generated art, and how it can be used in various industries.
Table of Contents
What is AI-Generated Art?
AI-generated art refers to creative works produced by artificial intelligence algorithms, either independently or in collaboration with human artists. This innovative approach to art-making utilises advanced neural networks and machine learning techniques to generate unique visual compositions, often resembling traditional artistic styles.
The Rise of AI-Generated Art
Over the last decade, AI-generated art has gained significant attention and recognition in the art world, with pieces being showcased in galleries, museums, and even auctioned for substantial sums.
The development of AI-generated art has been driven by the rapid advancements in AI research, particularly deep learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs). These sophisticated algorithms have enabled the creation of strikingly realistic and imaginative pieces of art, pushing the boundaries of what was previously thought possible in the realm of artistic expression. As a result, AI-generated art is quickly becoming a prominent and influential force within the contemporary art scene.
Platforms to Make AI Generated Art
There are various platforms available for creating AI-generated art. Here’s a list of some popular ones:
- RunwayML – A user-friendly platform that offers a wide range of machine learning models for creating AI-generated art, including image synthesis, style transfer, and object detection.
- DALL-E – Developed by OpenAI, DALL-E is an AI model capable of generating images from text descriptions, allowing for the creation of highly customised and unique artwork.
- Mid-Journey Bot – Mid-Journey Bot is an AI-driven platform that creates intriguing and engaging digital paintings using a blend of user input and machine learning algorithms. Users can influence the AI’s decision-making to generate unique artwork.
- Artbreeder – Artbreeder uses Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to create AI-generated art by blending and evolving existing images.
- Deep Dream Generator – DeepDream is a popular AI art tool that applies a neural network to transform images and create dream-like visuals.
- Paints Chainer – An online platform for creating AI-generated watercolour paintings from simple line art sketches.
- Night Cafe Creator – Offers various AI art tools, including style transfer, image synthesis, and AI-generated abstract art.
- VQGAN+CLIP – A combination of the VQGAN and CLIP models by OpenAI, this tool generates images based on textual descriptions and can be run locally or in Google Colab notebooks.
- Wombo Dream – Wombo Dream is an AI art platform that allows users to create unique and original artwork by entering a brief description or keyword.
- Adobe Firefly – Please note that Adobe Firefly is a newer AI-generated art platform. Adobe does also offer a variety of creative tools, such as Photoshop and Illustrator, that can be used in conjunction with AI-generated art or to create digital art manually.
- DeepArt.io – This platform allows you to create AI-generated art by applying the style of one image to the content of another using neural style transfer.
Please note that some of these platforms might require basic programming knowledge, access to APIs, or specific hardware to run the models. Additionally, always consider the ethical implications and copyright issues associated with creating and sharing AI-generated art.
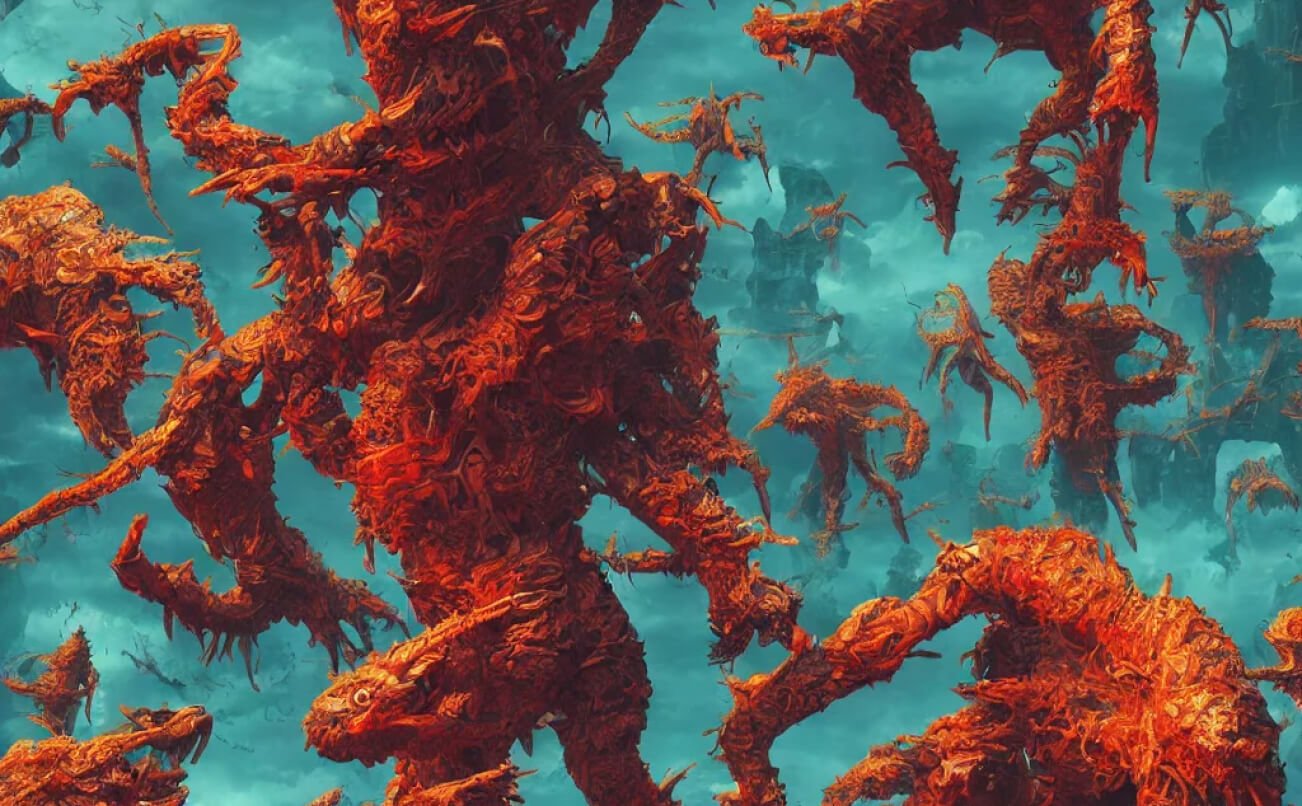

Source: Runway ML
Benefits of AI-Generated Art
Expanding Creative Possibilities
AI-generated art opens up a vast array of creative possibilities for artists, allowing them to explore new styles, techniques, and concepts. By using AI as a tool, artists can push the boundaries of their imagination and create pieces that may have been impossible or extremely time-consuming using traditional methods. This fusion of human creativity and AI-driven innovation results in a symbiotic relationship that can lead to groundbreaking artistic expressions.
Democratisation of Art
The rise of AI-generated art has the potential to democratise the art world by making the creation and appreciation of art more accessible to a wider audience. AI algorithms can analyse and learn from vast datasets of existing art, enabling the creation of compelling pieces without the need for years of artistic training. This development allows aspiring artists and enthusiasts to produce and engage with art in new and exciting ways, regardless of their background or experience level.
Commercial Applications
AI-generated art has various commercial applications, from advertising and marketing to interior design and entertainment. Companies can leverage AI-generated visuals to create eye-catching advertisements, while designers can use AI-generated art to develop unique and dynamic spaces. In the entertainment industry, AI-generated art can be used for film, television, and video game assets, significantly reducing production costs and time.
Negatives of AI-Generated Art
Authenticity and Originality
One of the primary concerns surrounding AI-generated art is the question of authenticity and originality. Critics argue that, since the artwork is produced by an algorithm rather than a human hand, it lacks the emotional depth and personal connection associated with traditional art forms. Additionally, as AI algorithms often learn from existing artistic works, the resulting creations may be perceived as derivative or lacking in true originality.
Intellectual Property and Copyright
AI-generated art raises complex legal questions related to intellectual property and copyright. Determining the ownership and rights associated with an AI-generated piece can be challenging, as it is unclear whether the credit should go to the AI developer, the user who initiated the creative process, or even the AI itself. This ambiguity can lead to disputes and hinder the commercialisation and distribution of AI-generated art.
Potential Job Displacement
As AI-generated art becomes more sophisticated and widely adopted, there is a growing concern that it may displace human artists in certain industries. While AI-generated art has the potential to democratise art creation, it may also lead to increased competition and reduced opportunities for traditional artists, particularly in fields like graphic design, advertising, and entertainment.
The Future of AI-Generated Art in the World
Education and Skill Development
AI-generated art has the potential to revolutionise art education and skill development. By incorporating AI tools into art curricula, educators can provide students with new ways to learn and experiment with various techniques and styles. This can help students develop a broader understanding of art and foster innovation within the field.
Magic Write offers AI-generated art education with tailored content on art techniques, creativity exercises, and art history. It provides prompts, tips, and guides for students and educators of all levels, fostering creativity and empathy in artistic practice.
Collaborative Art Projects
AI-generated art can foster collaboration between artists, technologists, and researchers, leading to innovative interdisciplinary projects. By combining their expertise, these professionals can push the boundaries of artistic expression and create unique works that challenge traditional notions of art. AI-generated art has the potential to facilitate the development of new artistic movements that redefine the way we perceive and engage with art.
Ethical Considerations
As AI-generated art continues to grow in prominence, it is crucial to address the ethical concerns that arise from its use. Developing guidelines and best practices for the responsible creation and use of AI-generated art can help mitigate potential negative impacts on artists, intellectual property rights, and cultural heritage. Open dialogue and collaboration among artists, AI developers, policymakers, and other stakeholders will be essential in shaping the future of AI-generated art in a way that is both innovative and respectful of artistic traditions.
The Soul of Artistic Expression: A Perspective from Traditional Printmaking
The Essence of Artistry Beyond AI Capabilities
In the ever-evolving landscape of art, the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has introduced a paradigm shift, particularly in the realm of visual creation. As a traditional printmaker, my perspective is deeply rooted in the tactile and nuanced world of printmaking, a craft that demands not just skill, but an intimate connection with the process and the medium. The essence of traditional art forms lies in their ability to convey the soul of the artist, a facet that is intrinsically human and often irreplaceable by AI.
Printmaking, a discipline that can span days, weeks or even months to complete a single piece, is a testament to the patience, dedication, and emotional investment of the artist. Each stroke, impression, and colour choice is a deliberate and thoughtful decision, often influenced by the artist’s emotions, experiences, and personal journey. This process, rich in texture and depth, is not just about the final artwork but about the journey of its creation. It is a narrative, a piece of the artist’s soul transformed into a tangible form.
In contrast, AI-generated art, while remarkable in its capacity to replicate styles and techniques, lacks this crucial element, the soul of creation. AI, with its algorithms and data-driven processes, can mimic the appearance of traditional printmaking methods in mere seconds. However, it cannot replicate the depth of human emotion and the unique perspective that an artist brings to their work. The AI’s creation is devoid of the personal touch, the subtle imperfections, and the emotional narrative that gives traditional artwork its character and appeal.
This is not to undermine the technological marvel that AI art represents, but rather to highlight a fundamental difference. AI art is a product of programming and algorithms, a synthesis of existing styles and elements. It is a showcase of technological prowess but not a conduit of human emotion and experience. As artists, we understand that art is not merely about the visual appeal; it is about the story, the struggle, the joy, and the pain that goes into creating something truly unique.
While AI can replicate the look of traditional art forms, it cannot capture the soul that comes from the human touch. The emotional depth, personal connection, and narrative that are embedded in each brushstroke, ink splotch, or carved line in printmaking are what truly make art resonate with its audience. It’s a reminder that in a world increasingly driven by technology, the human element in art remains not just relevant, but irreplaceable.
Conclusion
AI-generated art represents a groundbreaking fusion of technology and creativity, with the potential to transform the art world in profound ways. Its benefits include expanded creative possibilities, democratisation of art, and commercial applications, while its negatives encompass issues of authenticity, originality, intellectual property, and potential job displacement. As AI-generated art continues to evolve, it is essential to balance innovation with ethical considerations and ensure that this revolutionary creative force contributes positively to the global artistic landscape.